 Saving On Energy Costs This Winter
Saving On Energy Costs This Winter
Winter is fast approaching. If you’ve questioned whether your house is insulated enough to provide you with warmth at home and save money on your heating bills, now is the time to understand the R-Value of your home and to deploy some strategies that will help with heating your home and lowering your heating costs. The energy saving tips in this article and an understanding of R-Value and insulation (explained below) will get you started for the sake of your personal comfort, and to ward off a scary heating bill.
10 Ways to Save on Energy Costs This Winter
- Use the sun for free heat. …
- Bundle up with warm accessories. …
- Use ceiling fans to your advantage. …
- Adjust the thermostat at night. …
- Only heat the rooms you use. …
- Keep your furnace clean and unblocked. …
- Get a humidifier to add moisture to the air. …
- Invest in insulation.
- Decorate with LED lights for the holidays.
- Only use exhaust fans when necessary.
Click this link from US News for more information on these suggestions.
Insulation R-Value Defined
Energy efficiency has become an increasing concern to homeowners and the Real Estate and Property Insurance Industries. The performance of the insulation products installed in a building or dwelling are important factors to be considered when building, purchasing, or renovating a home or commercial property.
R-Value Defined
R–Value is defined as “The measurement used when quantifying the level of a specific material’s thermal resistance”.
How Does R-Value Relate to Insulation?
The function of insulation is to provide resistance to the flow of heat, and R-Value is the measure a material’s resistance to this heat flow.
A high R-value equates to higher resistance to heat flow. An insulation material’s R- Value, in conjunction with where and how it is installed, determines its overall effectiveness.
Quick Fact
Heating and cooling costs for a typical home in the US account for approximately 65% of the home’s total monthly energy usage.
Factors to Consider Regarding Thermal Resistance
 When considering R-value as a means to determine the thermal resistance of a building component, there are other factors that must also be taken into account. While R-values are an excellent guide for comparing the attributes of different insulation products, they apply only when the insulation is properly installed.
When considering R-value as a means to determine the thermal resistance of a building component, there are other factors that must also be taken into account. While R-values are an excellent guide for comparing the attributes of different insulation products, they apply only when the insulation is properly installed.
• For example, if two layers of insulation are compacted and forced into the space intended for only one layer, the R-value does not double.
• Likewise, if a single layer of insulation is compressed during installation, it will not be as effective. Stuffing “batt”-type insulation sized for 5 inches into a 4-inch wall cavity will actually lower its R-value!
• Ensuring that insulation is correctly installed will help allow the product’s full benefits to be realized.
 Calculating and Converting R-Value
Calculating and Converting R-Value
The equation used to calculate R-value can be helpful not only to Industry Professionals, but it can be helpful to Homeowners as well.
If the R-Value of the insulation is known, the following equation can be used to help calculate heat loss. The equation for determining R-value is as follows: R-Value = Temperature Difference x Area x Time
Heat Loss
- The Temperature Difference is expressed as T (“Delta T”) and is measured in degrees Fahrenheit (Deg F)
- The Area is expressed as A and is measured in Square Feet (Sq Ft)
- The Time is expressed as T and is measured in Hours (H) The Heat Loss is expressed as L and is measured in British Thermal Units (BTU)
- R-Value = T x A x T / L
Current Regulations Regarding R-Value
In the 1970s, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) created a rule requiring insulation manufacturers to disclose the R-Value of insulation material. This was intended to protect purchasers from false manufacturer claims, as well as to create a standard by which insulation products could be compared. The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) regularly issues recommendations for insulation R-values in new and existing homes. The recommendations are based on a comparison of the cost for installing insulation versus potential future energy savings.
Quick Fact
The DOE R-Value recommendations for attics, cathedral ceilings, walls and floors are generally greater than what is actually required by most current building codes.
R-Value Thickness Comparison Matrix
Below is a simple matrix that can useful in determining the R-Value of a material as compared to its thickness:
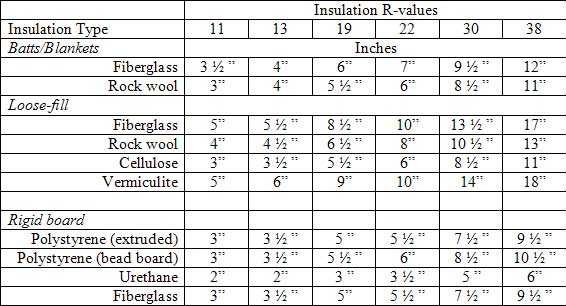
Knowledge of R-value ratings can be useful, especially when comparing the effectiveness of insulation products, but understanding a bit about how other factors affect a building component’s thermal resistance is important if insulation is to be used to its full benefit. Industry Professionals who are familiar with the basics of insulation R- values can provide “value-added” to their clients should questions regarding a property’s energy efficiency arise.